In the ever-evolving world of solar energy, technological advancements are continuously improving the way we harness the sun’s power. One such innovation is the dual-axis solar tracker, a device designed to optimize solar panel performance by tracking the sun’s movement throughout the day and across seasons. This article will explore how dual-axis solar trackers work, their benefits, types, and their impact on solar energy generation.
1. Introduction to Solar Trackers
1.1 What Are Solar Trackers?
Solar trackers are mechanical devices that adjust the position of solar panels throughout the day to follow the sun’s movement. The goal of using solar trackers is to increase the efficiency of solar energy systems by ensuring that solar panels are always oriented towards the sun, maximizing exposure to sunlight.
1.2 The Importance of Solar Tracking Systems
Solar tracking systems play a crucial role in improving the overall performance of solar energy systems, particularly in areas with variable weather conditions or where sunlight is not always consistent. By optimizing the angle at which solar panels capture sunlight, trackers can increase the energy output of a solar power system by up to 30% compared to fixed systems.
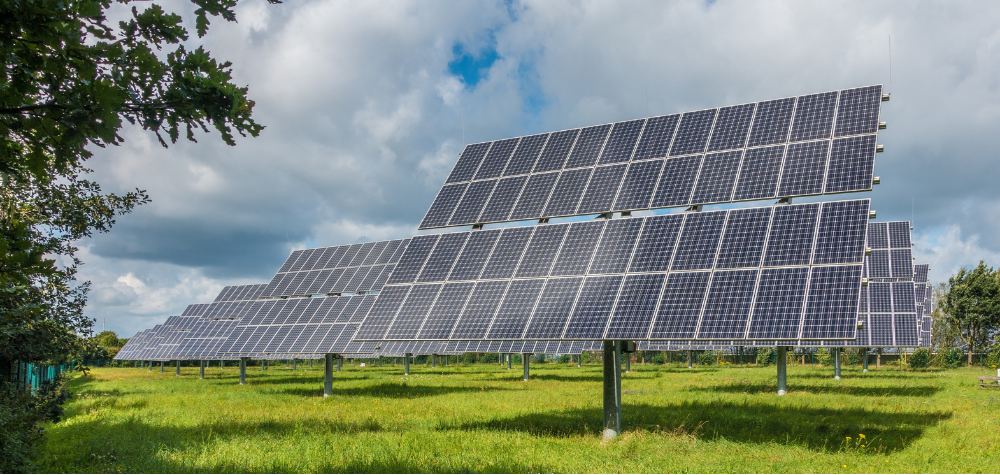

2. What is a Dual-Axis Solar Tracker?
2.1 How Dual-Axis Trackers Work
A dual-axis solar tracker is designed to move both horizontally and vertically, enabling solar panels to track the sun in both east-west and north-south directions. This allows the tracker to follow the sun’s trajectory throughout the day and adjust for seasonal variations, providing maximum sunlight exposure year-round.
2.2 Difference Between Single-Axis and Dual-Axis Trackers
- Single-Axis Trackers: These move the solar panels on one axis, usually from east to west, following the sun’s path during the day. They provide significant gains in efficiency compared to fixed systems but do not adjust for seasonal variations in the sun’s angle.
- Dual-Axis Trackers: These trackers, in contrast, move the panels both horizontally and vertically. They can track the sun across the sky during the day and also adjust for seasonal changes, providing even greater energy efficiency than single-axis systems.
3. Key Advantages of Dual-Axis Solar Trackers
3.1 Improved Energy Efficiency
The primary advantage of dual-axis solar trackers is their ability to maximize the exposure of solar panels to the sun. By tracking both the daily movement and seasonal shifts in the sun’s position, these trackers significantly boost energy production.
3.2 Maximizing Solar Exposure
Unlike fixed or single-axis systems, dual-axis trackers ensure that the solar panels are always facing the sun, regardless of time of day or time of year. This maximizes the amount of sunlight captured and converted into electricity, resulting in higher energy yields.
3.3 Reduction in Land Area Usage
Dual-axis trackers can concentrate solar panels in a smaller area because they ensure optimal panel alignment. This allows for a more efficient use of land, which is especially beneficial for large-scale solar farms.
3.4 Enhanced Energy Yield
Studies show that dual-axis solar trackers can increase energy yield by 35% or more compared to fixed-panel systems. This is because they more effectively capture sunlight throughout the day and across the seasons, providing more consistent energy output.
4. Challenges of Dual-Axis Solar Trackers
4.1 Higher Initial Costs
Dual-axis solar trackers are more expensive than fixed or single-axis systems, both in terms of the initial cost and installation expenses. The added mechanical complexity and additional components increase the upfront investment.
4.2 Increased Maintenance Needs
Due to their moving parts and sophisticated control systems, dual-axis trackers require more maintenance than fixed or single-axis systems. Regular inspection and servicing are essential to ensure their long-term functionality.
4.3 Space and Structural Considerations
Although dual-axis trackers save on land area in the long run, they require more space for movement during the tracking process. Additionally, the structural integrity of the support framework needs to be robust enough to withstand the added stress from the motion and weather conditions.
5. Components of a Dual-Axis Solar Tracker
5.1 Actuators
Actuators are devices that move the solar panels in response to commands from the control system. In dual-axis trackers, actuators are responsible for adjusting the panel’s position both vertically and horizontally.
5.2 Sensors
Sensors play a critical role in detecting the sun’s position in the sky. The sensors feed information to the tracker’s control system, allowing the panels to adjust their position accordingly throughout the day.
5.3 Control Systems
The control system is the brain of the tracker. It processes the data received from the sensors and commands the actuators to adjust the position of the panels.
5.4 Mounting Structures
The mounting structure is the foundation that holds the solar panels and the tracking system. It needs to be durable and capable of supporting the movement of the panels without compromising stability.
6. Applications of Dual-Axis Solar Trackers
6.1 Utility-Scale Solar Farms
Dual-axis trackers are especially useful for large utility-scale solar farms where maximizing energy generation is a priority. The ability to generate more energy per square meter of land is a significant advantage in these large installations.
6.2 Residential Solar Applications
While residential use of dual-axis trackers is less common due to higher costs and space requirements, some homeowners opt for dual-axis systems to maximize energy production, especially in regions with limited roof space.
6.3 Commercial Solar Installations
For commercial installations, dual-axis trackers offer a good balance between energy production and space optimization. Businesses seeking to reduce energy costs and improve their environmental footprint can benefit from the increased efficiency.
7. Comparison of Dual-Axis Solar Trackers with Other Solar Technologies
7.1 Comparing Dual-Axis to Fixed Solar Panels
- Fixed panels are cheaper and simpler to install but do not benefit from tracking the sun.
- Dual-axis trackers are more expensive but provide significantly better energy yield due to their ability to follow the sun throughout the day.
7.2 Dual-Axis vs. Single-Axis Trackers
- Single-axis trackers are more cost-effective and simpler to maintain but offer less efficiency than dual-axis trackers, which can adjust in two directions for greater accuracy and energy yield.
8. How to Choose the Right Solar Tracker for Your Project
8.1 Site Analysis and Considerations
When choosing a solar tracker, the specific site conditions, such as available land area, sun exposure, and climate, should be taken into account to determine the best type of tracker.
8.2 Budget and Cost-Benefit Analysis
It is important to evaluate the budget for the project and assess whether the additional cost of a dual-axis tracker can be justified by the potential increase in energy production and return on investment.
9. Future of Dual-Axis Solar Trackers
9.1 Technological Advancements
Future developments in materials and automation are likely to make dual-axis trackers more affordable and efficient. Innovations such as more durable components and advanced sensors will continue to enhance their performance.
9.2 Trends in the Solar Industry
With the growing push for renewable energy, the demand for high-efficiency systems like dual-axis trackers is expected to increase, driving further research and development in the field.
10. Conclusion
10.1 Final Thoughts
Dual-axis solar trackers represent a significant advancement in solar technology. Their ability to maximize energy production by following the sun in two directions makes them a valuable addition to solar energy systems, particularly in large-scale installations.
10.2 The Growing Role of Solar Trackers in Renewable Energy
As the world continues to embrace renewable energy, dual-axis solar trackers will play an increasingly important role in ensuring that we get the most out of solar energy, helping to meet global energy demands in a sustainable way.